Annex
1 Application
These Guidelines apply to all ships and provide the minimum recommended level of maintenance and inspections for fire protection systems and appliances. This information may be used as a basis for the ship's onboard maintenance plan required by SOLAS regulation II-2/14. These Guidelines do not address maintenance and inspection of fixed carbon dioxide systems or portable fire extinguishers. Refer to the comprehensive instructions provided in the Guidelines for the maintenance and inspections of fixed carbon dioxide fire-extinguishing systems (MSC.1/Circ.1318) for fixed carbon dioxide systems, and in the Improved Guidelines for marine portable fire extinguishers (resolution A.951(23)) for portable fire extinguishers.
2 Operational readiness
All fire protection systems and appliances should at all times be in good order and readily available for immediate use while the ship is in service. If a fire protection system is undergoing maintenance, testing or repair, then suitable arrangements should be made to ensure safety is not diminished through the provision of alternate fixed or portable fire protection equipment or other measures. The onboard maintenance plan should include provisions for this purpose.
3 Maintenance and testing
3.1 Onboard maintenance and inspections should be carried out in accordance with the ship's maintenance plan, which should include the minimum elements listed in sections 4 to 10 of these Guidelines.
3.2 Certain maintenance procedures and inspections may be performed by competent crew members who have completed an advanced fire-fighting training course, while others should be performed by persons specially trained in the maintenance of such systems. The onboard maintenance plan should indicate which parts of the recommended inspections and maintenance are to be completed by trained personnel.
3.3 Inspections should be carried out by the crew to ensure that the indicated weekly, monthly, quarterly, annual, two-year, five-year and ten-year actions are taken for the specified equipment, if provided. Records of the inspections should be carried on board the ship, or may be computer-based. In cases where the inspections and maintenance are carried out by trained service technicians other than the ship's crew, inspection reports should be provided at the completion of the testing.
3.4 In addition to the onboard maintenance and inspections stated in these guidelines, manufacturer's maintenance and inspection guidelines should be followed. The quality of water in automatic sprinkler systems is of particular importance and should be maintained in accordance with manufacturer guidelines. Records of water quality should be maintained on board in accordance with the manufacturer's guidelines
3.5 Where particular arrangements create practical difficulties, alternative testing and maintenance procedures should be to the satisfaction of the Administration.
4 Weekly testing and inspections
4.1 Fixed fire detection and alarm systems
Verify all fire detection and fire alarm control panel indicators are functional by operating the lamp/indicator test switch.
4.2 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
- verify all fixed fire-extinguishing system control panel indicators are functional by operating the lamp/indicator test switch; and
- verify all control/section valves are in the correct position.
4.3 Fire doors
Verify all fire door control panel indicators, if provided, are functional by operating the lamp/indicator switch.
4.4 Public address and general alarm systems
Verify all public address systems and general alarm systems are functioning properly.
4.5 Breathing apparatus
Examine all breathing apparatus and EEBD cylinder gauges to confirm they are in the correct pressure range.
4.6 Low-location lighting
Verify low-location lighting systems are functional by switching off normal lighting in selected locations.
4.7 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
- verify all control panel indicators and alarms are functional;
- visually inspect pump unit and its fittings; and
- check the pump unit valve positions, if valves are not locked, as applicable.
5 Monthly testing and inspections
Monthly inspections should be carried out to ensure that the indicated actions are taken for the specified equipment.
5.1 Fire mains, fire pumps, hydrants, hoses and nozzles
- verify all fire hydrants, hose and nozzles are in place, properly arranged, and are in serviceable condition;
- operate all fire pumps to confirm that they continue to supply adequate pressure; and
- emergency fire pump fuel supply adequate, and heating system in satisfactory condition, if applicable.
5.2 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
Verify containers/cylinders fitted with pressure gauges are in the proper range and the installation free from leakage.
5.3 Foam fire-extinguishing systems
Verify all control and section valves are in the proper open or closed position, and all pressure gauges are in the proper range.
5.4 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
- verify all control, pump unit and section valves are in the proper open or closed position;
- verify sprinkler pressure tanks or other means have correct levels of water;
- test automatic starting arrangements on all system pumps so designed;
- verify all standby pressure and air/gas pressure gauges are within the proper pressure ranges; and
- test a selected sample of system section valves for flow and proper initiation of alarms.
(Note – The valves selected for testing should be chosen to ensure that all valves are tested within a one-year period.)
5.5 Firefighter's outfits
Verify lockers providing storage for fire-fighting equipment contain their full inventory and equipment is in serviceable condition.
5.6 Fixed dry chemical powder systems
Verify all control and section valves are in the proper open or closed position, and all pressure gauges are in the proper range.
5.7 Fixed aerosol extinguishing systems
- verify all electrical connections and/or manual operating stations are properly arranged, and are in proper condition; and
- verify the actuation system/control panel circuits are within manufacturer's specifications.
5.8 Portable foam applicators
Verify all portable foam applicators are in place, properly arranged, and are in proper condition.
5.9 Wheeled (mobile) fire extinguishers
Verify all extinguishers are in place, properly arranged, and are in proper condition.
5.10 Fixed fire detection and alarm systems
Test a sample of detectors and manual call points so that all devices have been tested within five years. For very large systems the sample size should be determined by the Administration.
6 Quarterly testing and inspections
Quarterly inspections should be carried out to ensure that the indicated actions are taken for the specified equipment:
6.1 Fire mains, fire pumps, hydrants, hoses and nozzles
Verify international shore connection(s) is in serviceable condition.
6.2 Foam fire-extinguishing systems
Verify the proper quantity of foam concentrate is provided in the foam system storage tank.
6.3 Ventilation systems and fire dampers
Test all fire dampers for local operation.
6.4 Fire doors
Test all fire doors located in main vertical zone bulkheads for local operation.
6.5 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
Assess system water quality in the header tank and pump unit against the manufacturer's water quality guidelines.
7 Annual testing and inspections
Annual inspections should be carried out to ensure that the indicated actions are taken for the specified equipment:
7.1 Fire mains, fire pumps, hydrants, hoses and nozzles
- visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
- flow test all fire pumps for proper pressure and capacity. Test emergency fire pump with isolation valves closed;
- test all hydrant valves for proper operation;
- pressure test a sample of fire hoses at the maximum fire main pressure, so that all fire hoses are tested within five years;
- verify all fire pump relief valves, if provided, are properly set;
- examine all filters/strainers to verify they are free of debris and contamination; and
- nozzle size/type correct, maintained and working.
7.2 Fixed fire detection and fire alarm systems
- test all fire detection systems and fire detection systems used to automatically release fire-extinguishing systems for proper operation, as appropriate;
- visually inspect all accessible detectors for evidence of tampering obstruction, etc., so that all detectors are inspected within one year; and
- test emergency power supply switchover.
7.3 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
- visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
- externally examine all high pressure cylinders for evidence of damage or corrosion;
- check the hydrostatic test date of all storage containers;
- functionally test all fixed system audible and visual alarms;
- verify all control/section valves are in the correct position;
- check the connections of all pilot release piping and tubing for tightness;
- examine all flexible hoses in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations;
- test all fuel shut-off controls connected to fire-protection systems for proper operation;
- the boundaries of the protected space should be visually inspected to confirm that no modifications have been made to the enclosure that have created uncloseable openings that would render the system ineffective; and
- if cylinders are installed inside the protected space, verify the integrity of the double release lines inside the protected space, and check low pressure or circuit integrity monitors on release cabinet, as applicable.
7.4 Foam fire-extinguishing systems
- visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
- functionally test all fixed system audible alarms;
- flow test all water supply and foam pumps for proper pressure and capacity, and confirm flow at the required pressure in each section (Ensure all piping is thoroughly flushed with fresh water after service.);
- test all system cross connections to other sources of water supply for proper operation;
- verify all pump relief valves, if provided, are properly set;
- examine all filters/strainers to verify they are free of debris and contamination;
- verify all control/section valves are in the correct position;
- blow dry compressed air or nitrogen through the discharge piping or otherwise confirm the pipework and nozzles of high expansion foam systems are clear of any obstructions, debris and contamination. This may require the removal of nozzles, if applicable;
- take samples from all foam concentrates carried on board and subject them to the periodical control tests in MSC.1/Circ.1312, for low expansion foam, or MSC/Circ.670 for high expansion foam.
(Note: Except for non-alcohol resistant foam, the first test need not be conducted until 3 years after being supplied to the ship.); and
- test all fuel shut-off controls connected to fire-protection systems for proper operation.
7.5 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
.1 verify proper operation of all water mist, water-spray and sprinkler systems using the test valves for each section;
.2 visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
.3 externally examine all high pressure cylinders for evidence of damage or corrosion;
.4 check the hydrostatic test date of all high pressure cylinders;
.5 functionally test all fixed system audible and visual alarms;
.6 flow test all pumps for proper pressure and capacity;
.7 test all antifreeze systems for adequate freeze protection;
.8 test all system cross connections to other sources of water supply for proper operation;
.9 verify all pump relief valves, if provided, are properly set;
.10 examine all filters/strainers to verify they are free of debris and contamination;
.11 verify all control/section valves are in the correct position;
.12 blow dry compressed air or nitrogen through the discharge piping of dry pipe systems, or otherwise confirm the pipework and nozzles are clear of any obstructions. This may require the removal of nozzles, if applicable;
.13 test emergency power supply switchover, where applicable;
.14 visually inspect all sprinklers focusing in areas where sprinklers are subject to aggressive atmosphere (like saunas, spas, kitchen areas) and subject to physical damage (like luggage handling areas, gyms, play rooms, etc.) so that all sprinklers are inspected within one year. Sprinklers with obvious external damage, including paint, should be replaced and not included in the number of sprinklers tested in subparagraph .17;
.15 check for any changes that may affect the system such as obstructions by ventilation ducts, pipes, etc.;
.16 test a minimum of one section in each open head water mist system by flowing water through the nozzles. The sections tested should be chosen so that all sections are tested within a five-year period;
.17 test automatic sprinklers and automatic water mist nozzles in accordance with the following flow chart:
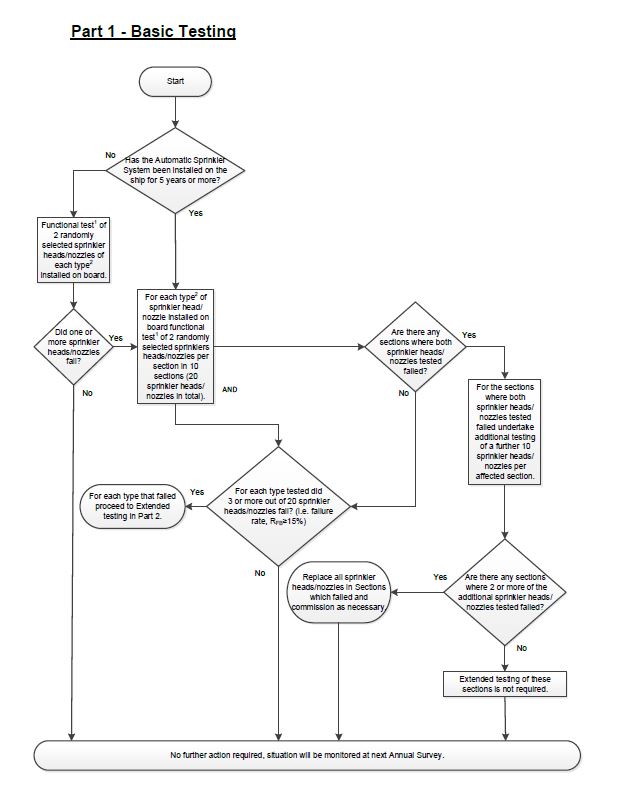

Explanatory notes to the flow chart
- Functional test is defined as a test that demonstrates the operation and flow ofwater from sprinkler head/nozzle.
- Type is defined as each different manufacturer model of sprinkler head/nozzle.
- Static/standby pressure is defined as the constant pressure maintained in the system at all times prior to activation.
- All testing should be carried out at static/standby pressure.
- Failure rate (RFB) is the number of sprinkler heads/nozzles to fail testing divided by test sample size multiplied by 100; and
.18 during basic testing, and extended testing when applicable, of automatic sprinkler heads/nozzles as outlined in subparagraph .17, water quality testing should be conducted in each corresponding piping section. Note – should a tested sprinkler fail, assessing the corresponding water quality at that time would assist in determining the cause of failure."
7.6 Ventilation systems and fire dampers
- test all fire dampers for remote operation;
- verify galley exhaust ducts and filters are free of grease build-up; and
- test all ventilation controls interconnected with fire-protection systems for proper operation.
7.7 Fire doors
Test all remotely controlled fire doors for proper release.
7.8 Breathing apparatus
- check breathing apparatus air recharging systems, if fitted, for air quality;
- check all breathing apparatus face masks and air demand valves are in serviceable condition; and
- check EEBDs according to maker's instructions.
7.9 Fixed dry chemical powder systems
- visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
- verify the pressure regulators are in proper order and within calibration; and
- agitate the dry chemical powder charge with nitrogen in accordance with system manufacturer's instructions.
(Note: Due to the powder's affinity for moisture, any nitrogen gas introduced for agitation must be moisture free.)
7.10 Fixed aerosol extinguishing systems
Verify condensed or dispersed aerosol generators have not exceeded their mandatory replacement date. Pneumatic or electric actuators should be demonstrated working, as far as practicable.
7.11 Portable foam applicators
- verify all portable foam applicators are set to the correct proportioning ratio for the foam concentrate supplied and the equipment is in proper order;
- verify all portable containers or portable tanks containing foam concentrate remain factory sealed, and the manufacturer's recommended service life interval has not been exceeded;
- portable containers or portable tanks containing foam concentrate, excluding protein based concentrates, less than 10 years old, that remain factory sealed can normally be accepted without the periodical foam control tests required in MSC.1/Circ.1312 being carried out;
- protein based foam concentrate portable containers and portable tanks should be thoroughly checked and, if more than five years old, the foam concentrate should be subjected to the periodical foam control tests required in MSC.1/Circ.1312, or renewed; and
- the foam concentrates of any non-sealed portable containers and portable tanks, and portable containers and portable tanks where production data is not documented, should be subjected to the periodical foam control tests required in MSC.1/Circ.1312.
7.12 Wheeled (mobile) fire extinguishers
- perform periodical inspections in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions;
- visually inspect all accessible components for proper condition;
- check the hydrostatic test date of each cylinder; and
- for dry powder extinguishers, invert extinguisher to ensure powder is agitated.
7.13 Galley and deep fat cooking fire-extinguishing systems
Check galley and deep fat cooking fire-extinguishing systems in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
8 Two-year testing and inspections
Two-year inspections should be carried out to ensure that the indicated actions are taken for the specified equipment.
8.1 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
- all high pressure extinguishing agents cylinders and pilot cylinders should be weighed or have their contents verified by other reliable means to confirm that the available charge in each is above 95 per cent of the nominal charge. Cylinders containing less than 95 per cent of the nominal charge should be refilled; and
- blow dry compressed air or nitrogen through the discharge piping or otherwise confirm the pipe work and nozzles are clear of any obstructions. This may require the removal of nozzles, if applicable.
8.2 Fixed dry chemical powder systems
- blow dry nitrogen through the discharge piping to confirm that the pipe work and nozzles are clear of any obstructions;
- operationally test local and remote controls and section valves;
- verify the contents of propellant gas cylinders (including remote operating stations);
- test a sample of dry chemical powder for moisture content; and
- subject the powder containment vessel, safety valve and discharge hoses to a full working pressure test.
9 Five-year service
At least once every five years, the following inspections should be carried out for the specified equipment.
9.1 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
Perform internal inspection of all control valves.
9.2 Foam fire-extinguishing systems
-
flush all ro-ro deck deluge system piping with water, drain and purge with air;
-
perform internal inspection of all control/section valves; water quality testing should be conducted in all corresponding piping sections, if not previously tested as outlined in paragraph 7.5.18 within the last five years;
- check all nozzles to prove they are clear of debris; and
- test all foam proportioners or other foam mixing devices to confirm that the mixing ratio tolerance is within +30 to -10% of the nominal mixing ratio defined by the system approval.
9.3 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
-
flush all ro-ro deck deluge system piping with water, drain and purge with air;
-
perform internal inspection of all control/section valves; water quality testing should be conducted in all corresponding piping sections, if not previously tested as outlined in paragraph 7.5.18 within the last five years;
-
check condition of any batteries, or renew in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations; and
-
for each section where the water is refilled after being drained or flushed, water quality should meet manufacturer's guidelines. Testing of the renewed water quality should be conducted and recorded as a new baseline reference to assist future water quality monitoring for each corresponding section.
9.4 Breathing apparatus
Perform hydrostatic testing of all steel self-contained breathing apparatus cylinders. Aluminium and composite cylinders should be tested to the satisfaction of the Administration.
9.5 Low-location lighting
Test the luminance of all systems in accordance with the procedures in resolution A.752(18).
9.6 Wheeled (mobile) fire extinguishers
Visually examine at least one extinguisher of each type manufactured in the same year and kept on board.
10 Ten-year service
At least once every 10 years, the following inspections should be carried out for the specified equipment:
10.1 Fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems
- perform a hydrostatic test and internal examination of 10 per cent of the system's extinguishing agent and pilot cylinders. If one or more cylinders fail, a total of 50 per cent of the onboard cylinders should be tested. If further cylinders fail, all cylinders should be tested;
- flexible hoses should be replaced at the intervals recommended by the manufacturer and not exceeding every 10 years; and
- if permitted by the Administration, visual inspection and NDT (non-destructive testing) of halon cylinders may be performed in lieu of hydrostatic testing.
10.2 Water mist, water spray and sprinkler systems
Perform a hydrostatic test and internal examination for gas and water pressure cylinders according to flag Administration guidelines or, where these do not exist, EN 1968:2002 + A1.
10.3 Fixed dry chemical powder systems
Subject all powder containment vessels to hydrostatic or non-destructive testing carried out by an accredited service agent.
10.4 Fixed aerosol extinguishing systems
Condensed or dispersed aerosol generators to be renewed in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations.
10.5 Wheeled (mobile) fire extinguishers
All extinguishers together with propellant cartridges should be hydrostatically tested by specially trained persons in accordance with recognized standards or the manufacturer's instructions.